Eutrophication Studies
Challenges with Eutrophication Studies
The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) describes nutrient pollution as “one of America’s most widespread, costly, and challenging environmental problems.” This issue is of significant concern world-wide, with considerable resources now being committed in Asia and Europe to study eutrophication in streams, rivers, lakes, bays and coastal waters and related economic, environmental and human health issues.

Solutions Provided by EEMS
EEMS has powerful water quality simulation and analysis features. EFDC+ provides simulation of 23 water quality (WQ) parameters, including a full sediment diagenesis model. The post-processing options for WQ includes 2-D plan (by layer or depth averaged), vertical section plots, and a range of animations. Unlike similar tools such as MIKE or DELFT, EEMS has all the tools available in one fully equipped package.
EEMS is regularly used to simulate the growth and decay of algae and the its impact on dissolved oxygen, as well as phosphorus and nitrogen cycles. The WQ sub-model is internally coupled with hydrodynamics and sediment transport sub-model to allow smooth exchange of constituents with the atmosphere and the sediment bed.
Example Studies
Typical examples of water quality studies include:
- Perdido Bay, Florida – D.O. and Nutrient TMDL Model Development
- Klosterman Bayou, Florida – D.O. and Nutrient TMDL Model Development
- Lake Taihu, China
- West Lake, Vietnam
Other Examples of Studies Done with EFDC:
- Illinois River Watershed
- Prediction of algal blooming using EFDC model: Case study in the Daoxiang Lake
- Algal bloom prediction of the lower Han River, Korea using the EFDC hydrodynamic and water quality model
Tenkiller Ferry Lake WQ Study, OK/IL, USA
DSI developed a linked watershed, hydrodynamic and water quality model of a portion of the Illinois Basin as part of development of a TMDL for Tenkiller Ferry Lake, OK. The Lake is identified as impaired because of elevated nutrients, and it is a high-priority target for TMDL development. The HSPF watershed model was used to simulate watershed runoff and point and nonpoint source loads from the watershed. The HSPF model was recalibrated to a 20 year simulation period. The HSPF provided flow, total phosphorus, total nitrogen and organic material loads. These HSPF results were then linked to the 3D EFDC+ water quality model flow of Lake Tenkiller. A two year simulation period was used for calibration of the EFDC water quality model. The calibrated model was then used to conduct load reduction scenarios as part of the TMDL process.
Little Bow River Water Quality Model Development, Alberta, Canada
The Little Bow River watershed is located in the headwaters of the Oldman River Basin in the southern region of the Province of Alberta. The watershed supports a wide variety of natural resources, including forests, minerals, wildlife, and agricultural lands. To support flood mitigation work related to Highwood-Little Bow diversion system and Little Bow River, a model was developed as an assessment tool to evaluate the existing flow and water quality condition in the upper Little Bow River and potential impact of various flood related management plans. The Environmental Fluid Dynamics Code (EFDC) platform was selected for the Little Bow River system.
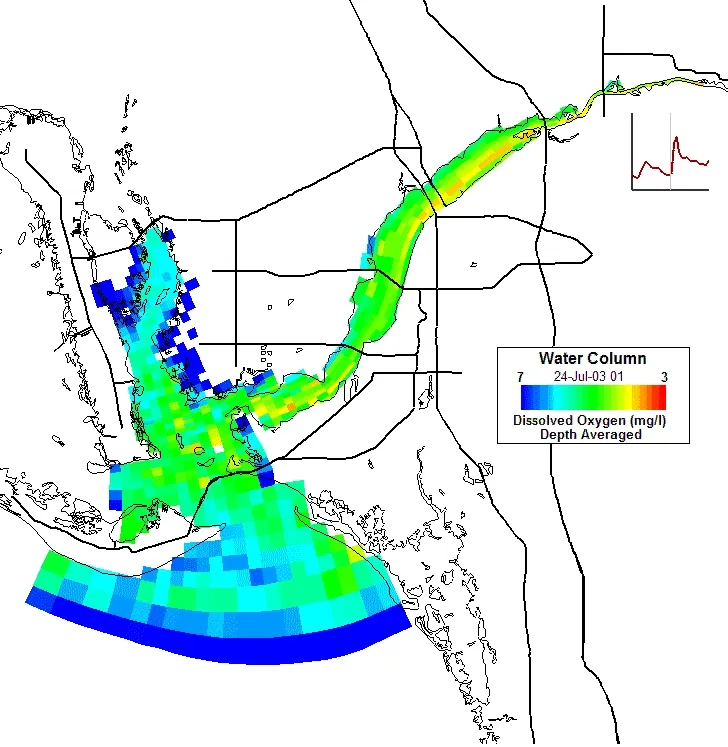
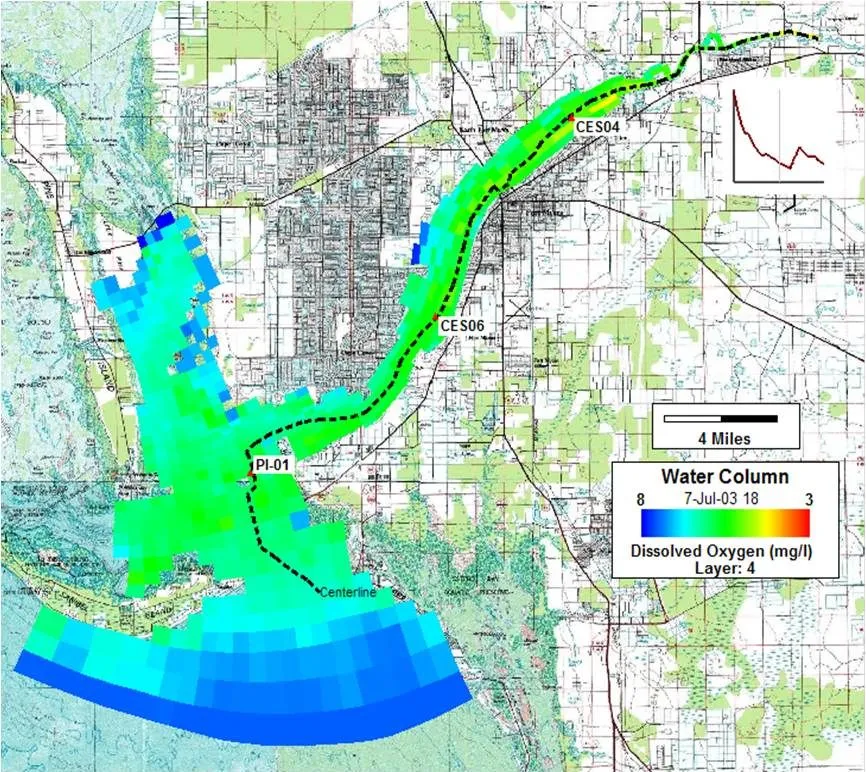
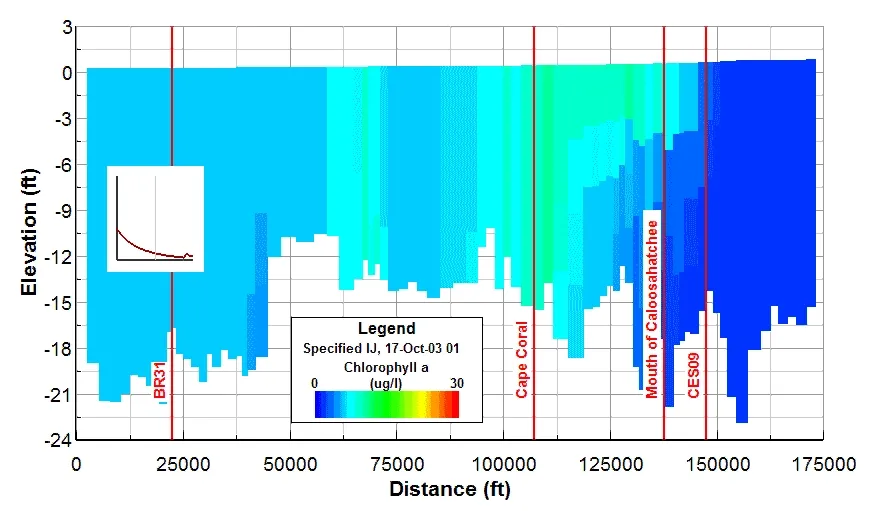
Caloosahatchee River Basin Hydrologic, Hydrodynamic and WQ Modeling, FL, USA
The Caloosahatchee River Basin , extending from Lake Okeechobee to San Carlos Bay on Florida’s west coast, has several Waterbody Identification units (WBIDs) included in the State of Florida’s 2004 list of impaired water bodies because of nutrient enrichment and low levels of dissolved oxygen. The tidal estuary of the Caloosahatchee River is characterized by freshwater inflow from Lake Okeechobee along the non-tidal portion of the river that receives agricultural wastewater discharge and run-off from the urbanized and developing areas around Ft Myers. As part of FDEP’s TMDL development process, DSI/Dynamic Solutions, LLC developed a linked HSPF watershed and EFDC hydrodynamic/water quality model of the 1,400 square mile Caloosahatchee watershed, river and estuary.
The images below demonstrate EE visualizations of WQ parameters from the TMDL study of Caloosahatchee Estuary, Florida. The plan view animation displays the depth averaged DO values as algal blooms form in the estuary. A track through the model domain has been defined by the user and a profile animation along that path shows chlorophyll a formation near the surface later in the same year.