EFDC+
Thermal Modeling
EFDC+ has been enhanced with a range of heat exchange options, providing you increased flexibility when simulating complex thermal systems.
New Surface Heat Exchange Options
EFDC+ has two surface heat exchange options, both of which allow for spatially and temporally varying surface heat exchange coefficients and light extinction factors. An equilibrium temperature approach was provided in 2008, and with the release of Version 8.3, EFDC+ now offers a new full heat exchange option. By comparison, with the exception of wind effects, the standard EFDC version only allows for heat exchange coefficients that are temporally and spatially constant.
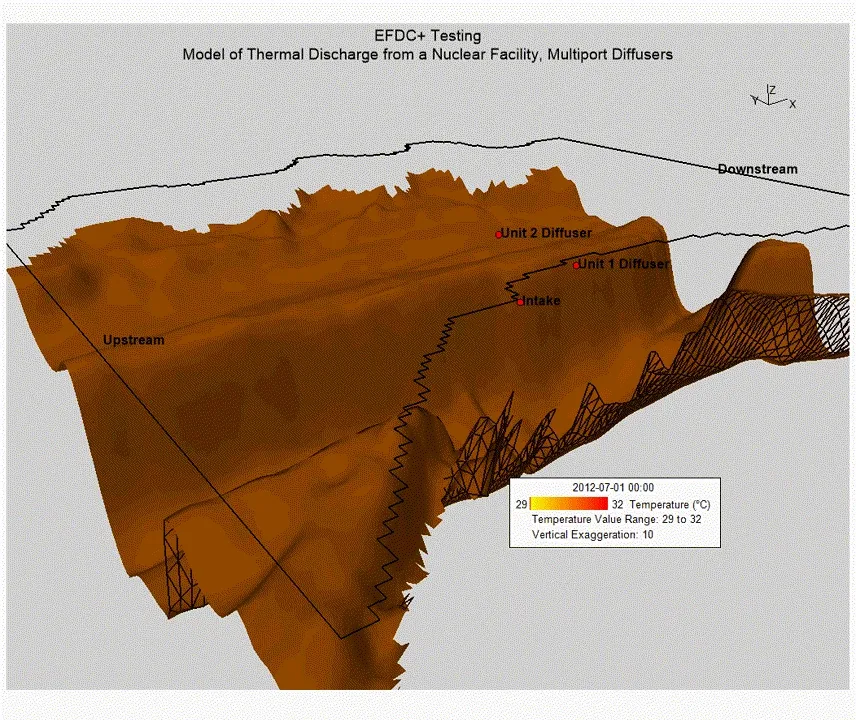
Heat Coupled Ice Modeling
EFDC+ implements a robust ice sub-model where ice formation and melt is simulated using the coupled heat model. This feature is not available in other versions of EFDC or other environmental hydrodynamic modeling tools such as MIKE3 or DELFT3D.
Forced Evaporation
Forced evaporation is defined as the additional evaporation in receiving waters due to increased temperatures from the discharge of heated cooling water. Federal and state agencies now consider forced evaporation to be a consumptive use for thermal electric power plants. EFDC+ has the necessary toolbox to provide spatial and temporal evaluations of forced evaporation.
