Challenges with Atmospheric Temperature Change
Changing atmospheric temperatures affects water temperature and has adverse impact on a wide range of aquatic life. Simulation of the thermal regime coupled with forecast temperature scenarios helps regulators minimize the impacts of climate change and evaluate mitigation options.
Solutions Provided by EEMS
The EFDC+ model has a proven capability of accurate thermal modeling for rivers, lakes and estuaries, including use in real-time systems. With EFDC+, users can also model steep sloping bathymetry and accurately reproduce the thermocline in a way not possible with similar models. Combined with a variety of calibration tools and habitat analysis tools, different scenarios affecting water temperatures can be easily compared.
Examples of Studies Done with EEMS
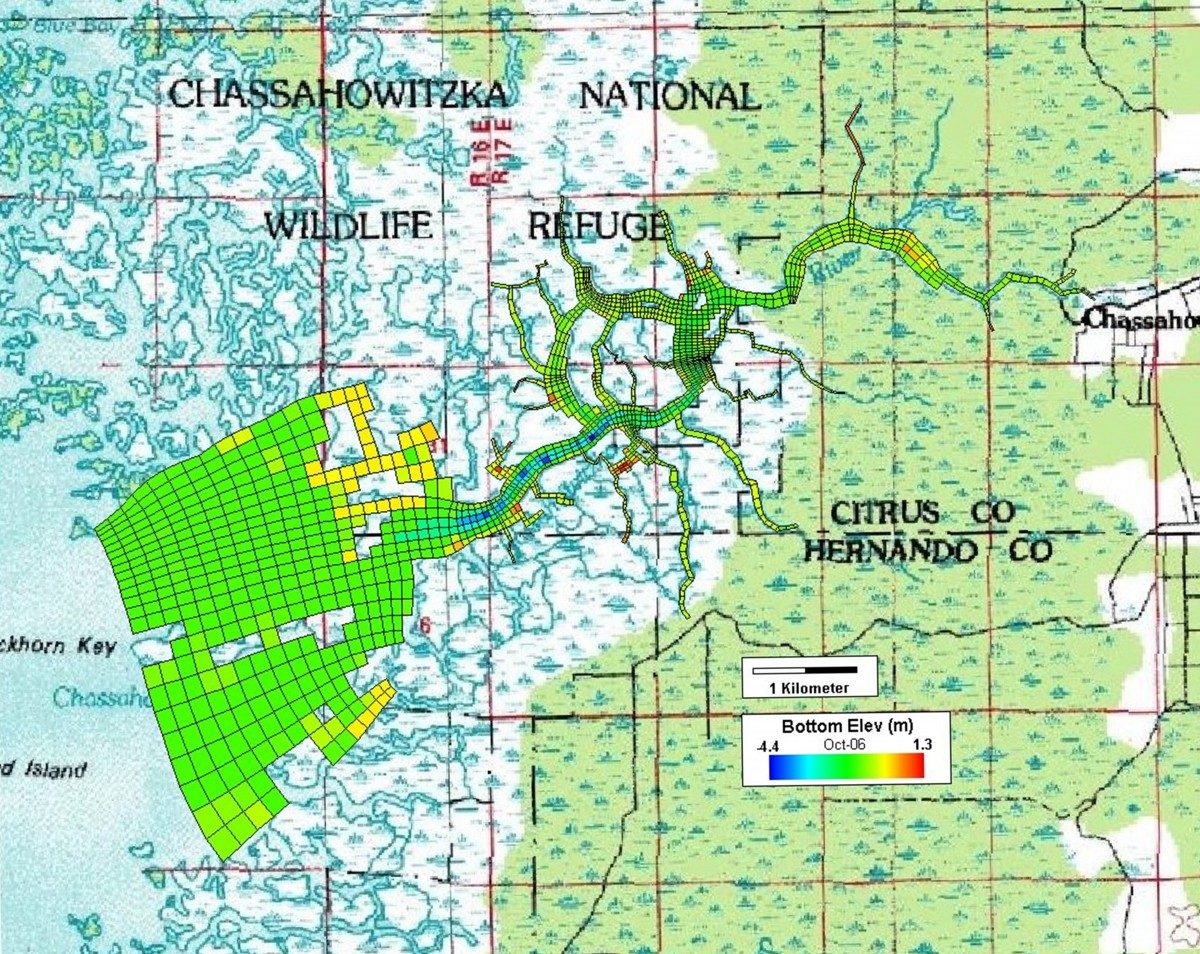
Impact of Groundwater Spring Flow Reductions on the Chassahowitzka River/Estuary System
Determination of the areas in the Chassahowitzka system that meet manatee habitat criteria during critical conditions from a 3D hydrodynamic (salinity and temperature) model using EEMS.
Real-time Thermal Hydrodynamic Model Decision Support Tool, AL, USA
EEMS was used to develop a real-time 3D hydrothermal model for Coosa River, AL, between Logan Martin Dam and Lay Dam. The model’s external forcing factors include flow releases from Logan Martin and Lay Dam, flows from tributaries, power plant withdrawal and temperature rise, and atmospheric conditions. The real-time model was calibrated against the field measurements of flows, water level, and water temperature. The model was developed to serve as a decision-making tool for Alabama Power Company (APC) electricity generation and assist in efficient operation of Logan Martin, Lay and Plant Gaston in order to meet generation needs while staying in thermal compliance at the monitoring buoy below Gaston. An online web interface was designed to visualize the results of the real-time EFDC+ model and provide quantitative comparisons to the thermal standard to help in real-time decision making. The web interface allows users to perform scenario analyses.
Download Example Models
Download an example model and run with the free EEMS Demo Version.
Lake Washington is the second largest natural lake in the State of Washington, USA. DSI developed a hydrodynamic model of this waterbody to determine with what degree of accuracy the prediction of the epilimnion and hypolimnion could be made using the new Sigma-Zed approach. A version of this model with reduced number of cells may be downloaded for users to see the advantages of this approach for themselves. Model output may be compared with data measured at the buoy at the lake’s centre. See here for more details.