Challenges with Salinity Intrusion
Salinity intrusion is of growing concern in many regions where natural fresh water flows are impacted because of direct human activity such urbanization and dam construction, as well as climate change. Mathematical model of these natural systems can be efficiently used for estimating and evaluating the nature of the salinity intrusions on a seasonal and long-term basis.
Solutions Provided by EEMS
EFDC+ accurately models fresh and saline water interactions in estuaries and river systems allowing users to develop well calibrated models of their waterbodies and evaluate the impacts of climatic change. Using the EFDC+ Sigma-Zed model allows highly realistic simulations of the stratification in the waterbody in comparison to similar modeling systems. EE provides a host of post-processing tools to better analyze and interpret the model results.
Examples of Studies Done with EEMS
Ocean Pointe Salinity Study
An EFDC+ model of a coastal region near Ocean Pointe, Hawaii, was developed with the objective of assessing the impact of major freshwater storm drains on the salinity patterns. These were evaluated relative to the salinity standards (>31.5 ppt) for coral reefs in the vicinity. The EFDC+ model was linked to the radiation shear stresses and other wave results from a REF/DIF model.
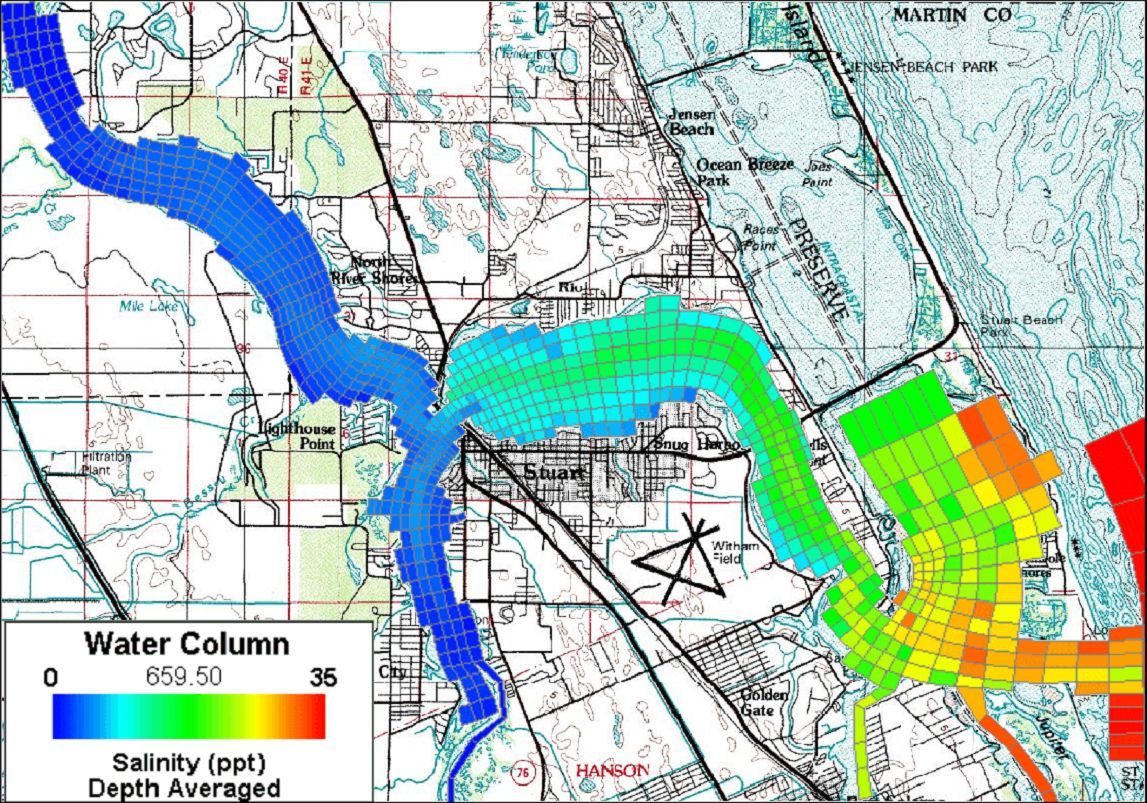
Lower St Johns Estuary Salinity Intrusion Study (FL, USA)
The objective of this modeling study was to develop a 3D hydrodynamic, salinity and temperature model to evaluate the effect of freshwater inflows, particularly high flow releases from Lake Okeechobee, on salinity distributions in the estuary. High flow events, by diluting salinity levels, adversely impact biologically sensitive habitats such as oyster beds and stands of submersed aquatic vegetation.
Groundwater Flow Reductions in Chassahowitzka Estuary System (FL, USA)
A 3D EFDC+ Model for salinity and temperature was built for Southwest Florida Water Management District, to help determine areas in the Chassahowitzka system that meet manatee habitat criteria during critical conditions. Furthermore, simulation was made for salinity changes and the resulting changes in the volume, area and shoreline lengths of salinity regimes due to reductions in spring flows, that are caused groundwater extractions and climate change.
Download Example EE Models
Download an example model and run with the free EEMS Demo Version.
This example model of the Tra Khuc Estuary in Vietnam demonstrates the coastal modeling capabilities of EEMS and shows salinity intrusion into the estuary. It also includes full sediment transport simulation.