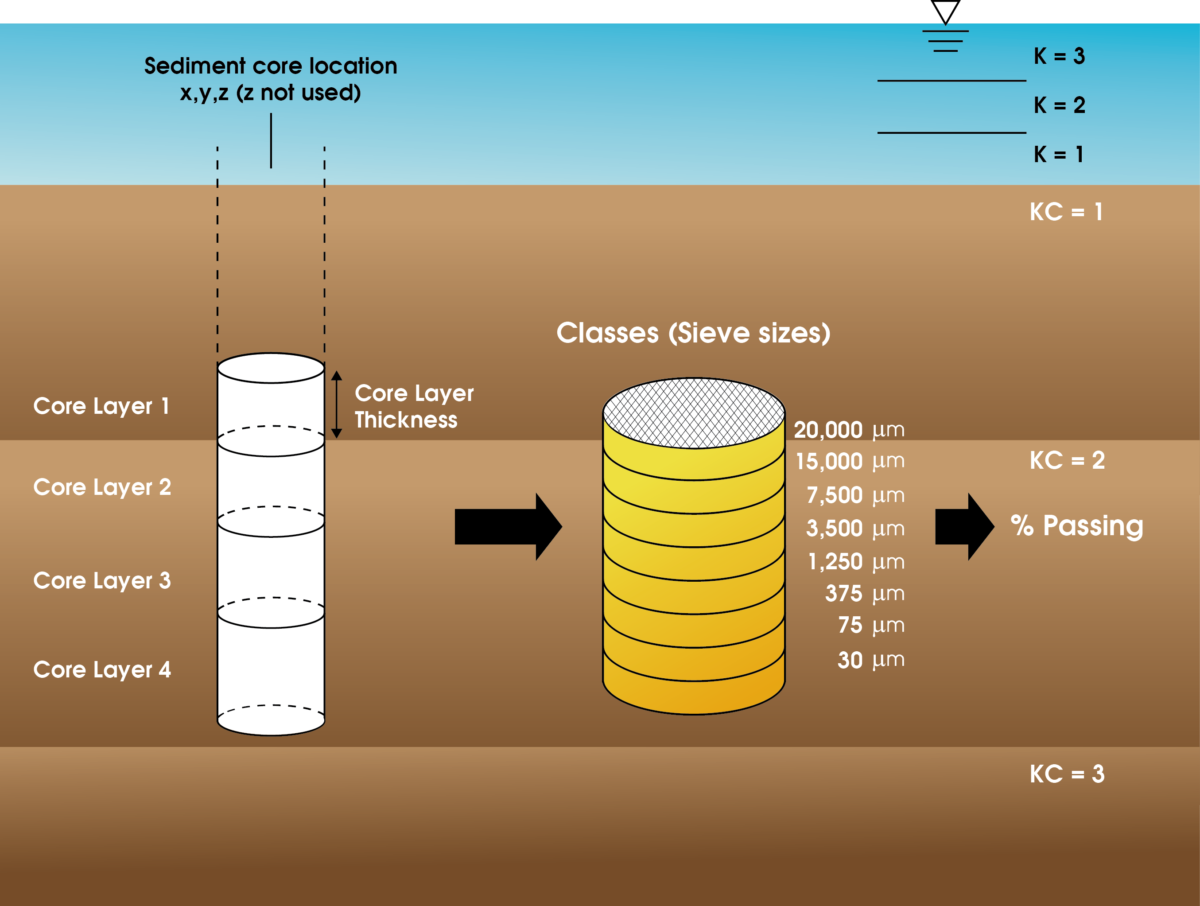
For sediment transport modeling, EFDC requires a modeler to define particle size classes and specify the median diameter for each class, which can represent the average behavior of the particles. A general approach to specify the median grain size for a modeling class i is

where the maxi and mini represent the upper and lower bounds of a modeling size class i, respectively.
Another approach uses an effective grain size for each modeling class based on the content fraction given data classes. For each modeling class i, the effective grain size di can be computed as

Where fj is fractional content of data class j, Gj is geometric mean diameter for data class j, and n is the number of data classes within a modeling size class i. This approach would be a better way when the high-resolution grain size distribution is available for given sediment data. Below table presents the median grain sizes for modeling size classes using example sediment data, and two approaches show different di values over the classes.