Challenges with Remedial Design
Industrial practices such as oil refineries and chemical plants commonly leave a long-term legacy of contaminated sediments. Sediment remediation is a costly and challenging undertaking. Design of remediation strategy involves methods to excavate and contain sediment hotspots, install permeable barriers, groundwater hydraulic containment systems, and isolate and cap the impacted sediments. 3D modeling of the hydrodynamics, sediment transport and specific contaminants is often required.
Solutions Provided by EEMS
EEMS has been used extensively in the simulation and analysis of contaminated sediment for remedial design studies. EEMS allows the user to accurately characterize the site conditions, with tools to support the data processing, model building and the simulation of the specific processes for transport of PCBs, dioxins, herbicides, and pesticides in 1-D, 2-D, and 3-D. EEMS helps in visualizing the lateral and vertical extent of toxics in the sediment bed. Comparison of scenarios for source removal actions, such as dredging, allows efficient use of resources and cost savings. Analysis of bed shear in the model domain helps determine shear stress on sediment caps.
EEMS is also used to evaluate recontamination scenarios in remedial design. The EFDC+ code includes several internal sub-models for simulating the transport and fate of toxic contaminants. A simple, single contaminant sub-model accounts for water and suspended sediment phase transport with equilibrium partitioning and a lumped first order reaction. Contaminant mass per unit area in the sediment bed is also simulated. A second, more complex, sub-model simulates the transport and fate of an arbitrary number of reacting contaminants in the water and sediment phases of both the water column and sediment bed. It includes the flexibility of simulating an arbitrary number of contaminants, and the improved accuracy of utilizing more complex three-dimensional physical transport fields in a highly accurate numerical transport scheme.
Examples of Studies Done with EEMS
Examples of some of the dozens of contaminated sediments projects carried out using EFDC+ include:
- Portland Harbor, OR, USA (client confidential)
- Newark Bay/Passaic River, NJ, USA (client confidential)
- Duwamish River, WA, USA (client confidential)
- Danang Airport Dioxin Investigation, Vietnam
- Bien Hoa Airport Dioxin Investigation, Vietnam
- Port Augusta Hydrodynamic Model and Mercury Study, Sicily, Italy
- Little Lake Butte de Morts Sediment Dynamics, WI, USA
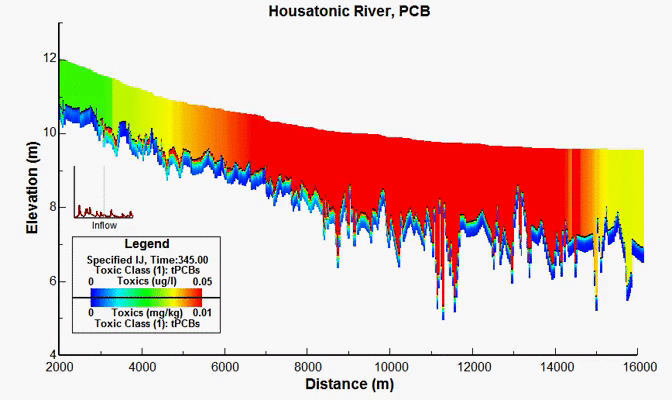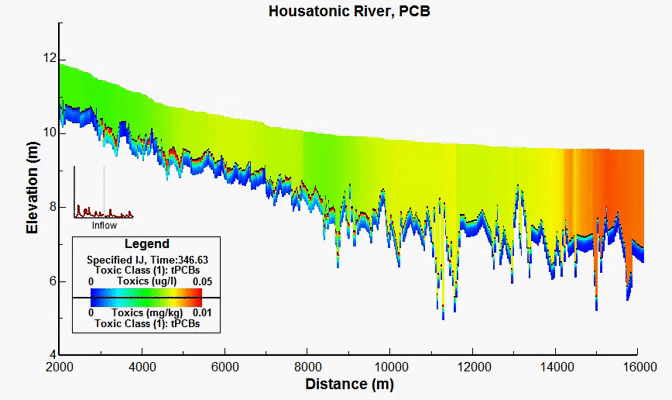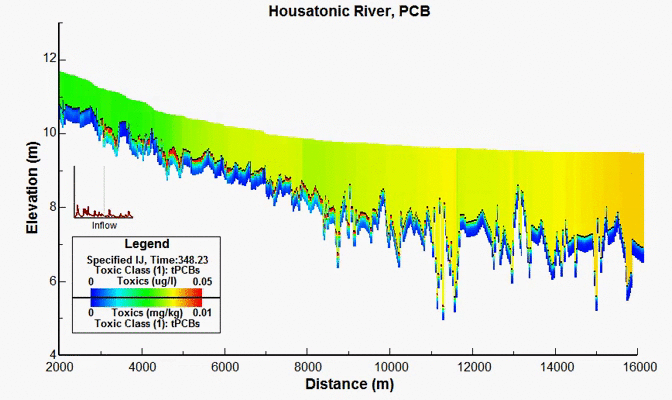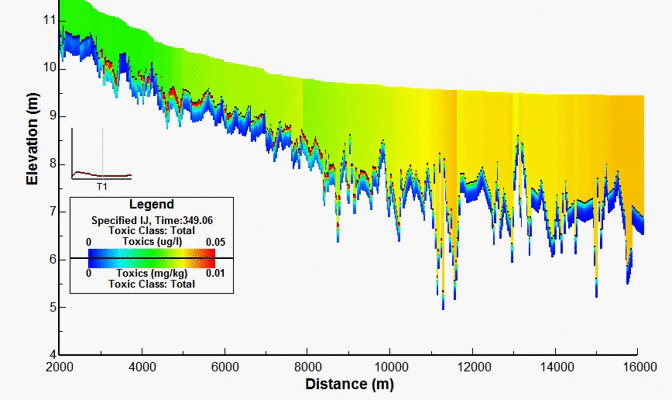
Housatonic River PCB Study, MA, USA
For decades, PCBs have been released onto the soil near and into the Housatonic River from a GE facility in Pittsfield, MA. In 1998, after years of scientific investigations and regulatory actions, a comprehensive agreement was reached between GE and various governmental entities, providing for the investigation and cleanup of the Housatonic River and associated areas. Under the terms of the Consent Decree, EPA conducted a detailed modeling study of hydrodynamics, sediment transport, and PCB fate and bioaccumulation in the Housatonic River below the confluence of the East and West Branches and encompassing watershed. EEMS was used in all aspects of work performed by the modeling team. DSI had responsibility for the development of the model grid, hydrodynamic model, sediment transport model, and the PCB transport and fate model.
Download Example EE Models
Download an example model and run with the free EEMS Demo Version.